Quiz
(focus is on the reading)
This quiz should be done individually with no discussion with other students. It is given on the honor system with my trust that you will not ask for or receive help. You may consult books (I recommend your text book) and information on the web. You may not post questions to receive answers. If you feel that you should clarify your answer or clarify you interpretation of the question, please write a short explanation.
Please note: There is not a resubmit on this quiz Please submit using the answer sheet provided at the site.
Question #1: The smallest usable unit of data such as a letter, number or special symbol is called a ___________________.
A) bit B) character C) address D) variable
Question #2: True or False: inv Ans + 20 is a valid
memory variable
T) True F) False
Question #3: You want to keep the social security number, name, job code and pay rate for your employees. What is the data hierarchy name for each of these data items?
A) field B) file or table C) record D) character
Question #4: Looking at the data in the problem
above: you want to store all of the information about a specific employee
together. What is the data hierarchy name for storing these fields together as
a unit?
A) field B) file or table C) record D) character
Question #5: Looking at the data in the problem above: you want to store all of the information about all of employees in your company together. What is the data hierarchy name for storing your employee data?
A) field B) file or table C) record D) character
Question #6: True or False: In most languages you can
code a calculation in either of the following ways:
ansWork
= numIn -15
numIn -
15 = ansWork
T) True F) False
Question #7: Errors in the use of the programming language such as word usage and grammar are called ____________ errors?
A) logic B) data C) development D) syntax
Question #8: Common tool(s) for planning the logic involved in developing a solution to a programming problem are ______________________.
A) flowchart B) compiler C) pseudocode D) both flowchart and pseudocode
Question #9: Data that is stored in locations in memory are called ______________ ? An example would be storing the result of a calculation in memory.
A) alpha B) instructions C) variables D) variables and instructions
Question #10: The program that is actually run or executed is the ________________ program.
A) high-level language B) object C) executable D) object or executable or machine language all apply
Question #11: The software that translates a high – level or source program into machine language is ___________ ?
A) compiler B) interpreter C) executer D) both compiler and interpreter apply
Question #12: When you test a machine language program with data, you are looking for _______ errors?
A) syntax B) logic C) compilar D) both syntax and logic apply
Question #13: A database is made up of a group of ______________ that hold the collection of data. For example, there might be one holding inventory information and one holding customer information.
A) tables B) columns C) variables D) none of the answers apply
Question #14: Calculating an answer and storing it to a named memory location is using ____________ ?
A) comparison B) equal C) assignment D) compiling
Question #15: True or False: You cannot execute a program to produce output if it has critical syntax errors.
T) True F) False
Question #16: A variable name can also be called a(n) ________________
A) byte B) record C) identifier D) assignment
Question #17: True or False: This structure processes
and then tests to see if the processing should be done again. The processing
will always be done at least once.
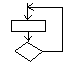
T) True F) False
Question #18: You use quotation marks to enclose ____________________ .
A) string or character constant B) numeric constant C) variable names
D) string or character or numeric constant
Question #19: In the example below, the = is called a(n) __________________.
ans = a + b
A) equal sign B) assignment sign C) comparison operator D) either an equal sign or an assignment sign
Question #20: The case structure is an alternative to a(n) _____________
A) series of calculations B) series of assignments C) series of selections
D) while loop
Question #21: True or False: This structure tests and
then processes. Processing continues while the condition is true. The
processing will always be done at least once.
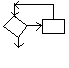
T) True F) False
Question #22: The three structures that define all programming logic are _____________, _____________, _________________.
A) selection, process, loop B) sequence, selection, loop C) sequence, iteration, loop
D) sequence, repetition, case
Question #23: When a structure contains another structure, it is called _____________.
A) stacking B) repetition C) selection D) nesting
Question #24: Which of the following is NOT an acceptable name for the structure that allows you to do the same set of instructions multiple times?
A) repetition B) iteration C) decision D) loop
Question #25: In structured programming, the first data input statement or read is separate from the data input statement or read statement for all of the other records. The first data input statement or read is called ______________.
A) priming read B) priming input C) initializing read D) all of the above
Question #26: A(n) _____________________ is used to show the relationship between modules.
A) logic flowchart B) data dictionary C) hierarchy chart D) print chart
Question #27: True or False: calc Reorder() is a valid name for a module according to the rules in your text.
T) True F) False
Question #28: When one module causes another module to execute, the first module is ___________ the second module.
A) defining B) reusing C) declaring D) calling
Question #29: True or False: Once you have designed the output, you need to look at the available input and see if you have the data available to produce the output.
T) True F) False
Question #30: Which of the following is NOT a reason to use modularization?
A) abstraction B) reusability of code C) encourages one programmer to develop all the code D) easier to identify structures
Question #31: True or False: In a printer spacing chart, each box represents a field that will be printed.
T) True F) False
Question #32: The part of documentation that lists all variable names in the program along with their type, size and description is called a _______________________.
A) data dictionary B) hierarchy chart C) user documentation manual D) GUI
Question #33: True or False: The program is written before the output is designed.
T) True F) False
Question #34: You have 100 records on your file or table and you are writing a report that is printing out the information from all 100 records. On the printer spacing chart, the line representing the data on the record is called the ______________________.
A) constant B) heading line C) detail line D) summary line
Question #35: True or False: You should not use embedded spaces in a variable name.
T) True F) False
Question #36: True or False: After reading an input record, the programmer should always check and see if the read was successful or whether EOF was encountered.
T) True F) False
Question #37: True or False: A good programming technique is to store modules separately and use code to include them in appropriate places in your program.
T) True F) False
Question #38: True or False: Some languages require you to specify the length of all variables, other languages assign a predetermined size depending on the type for some types of variables.
T) True F) False
Question #39: True or False: Giving a starting value to a variable is known as initializing the variable. The value in the variable can be changed as the program executes.
T) True F) False
Question #40: The modules of the mainline logic of a typical procedural program are ________________, __________________, _____________________.
A) housekeeping, setup, initialization B) housekeeping, processing, looping
C) housekeeping, processing, wrapup D) setup, initializing, looping